Definition of bathochromic in the Definitions.net dictionary. Meaning of bathochromic. What does bathochromic mean? Information and translations of bathochromic in the most comprehensive dictionary definitions resource on the web. Apr 22, 2020 Bathochromic shift (from Greek βαθύς bathys, 'deep'; and χρ?μα chrōma, 'color'; hence less common alternate spelling 'bathychromic') is a change of spectral band position in the absorption, reflectance, transmittance, or emission spectrum of a molecule to a longer wavelength (lower frequency).
Bathochromic shift (from Greek βαθύς bathys, 'deep'; and χρῶμα chrōma, 'color'; hence less common alternate spelling 'bathychromic') is a change of spectral band position in the absorption, reflectance, transmittance, or emission spectrum of a molecule to a longer wavelength (lower frequency).[1] Because the red color in the visible spectrum has a longer wavelength than most other colors, the effect is also commonly called a red shift.
Hypsochromic
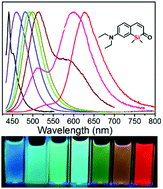
Hypsochromic shift is a change to shorter wavelength (higher frequency).
Bathochromic Shift Example
Conditions[edit]
It can occur because of a change in environmental conditions: for example, a change in solvent polarity will result in solvatochromism.[2]
A series of structurally-related molecules in a substitution series can also show a bathochromic shift. Bathochromic shift is a phenomenon seen in molecular spectra, not atomic spectra; it is thus more common to speak of the movement of the peaks in the spectrum rather than lines.
- where is the wavelength of the spectral peak of interest and
Detection[edit]
Bathochromic shift is typically demonstrated using a spectrophotometer, colorimeter, or spectroradiometer.
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^Kamlet, Mortimer J.; Taft, R. W. (1976). 'The solvatochromic comparison method. I. The .beta.-scale of solvent hydrogen-bond acceptor (HBA) basicities'. Journal of the American Chemical Society. 98 (2): 377–383. doi:10.1021/ja00418a009. ISSN0002-7863.
- ^Buncel, Erwin; Rajagopal, Srinivasan (1990). 'Solvatochromism and solvent polarity scales'. Accounts of Chemical Research. 23 (7): 226–231. doi:10.1021/ar00175a004. ISSN0001-4842.
Bathochromic Shift Definition
Hypsochromic shift (from ancient Greek ὕψος (upsos) 'height'; and χρῶμα chrōma, 'color') is a change of spectral band position in the absorption, reflectance, transmittance, or emission spectrum of a molecule to a shorter wavelength (higher frequency). Because the blue color in the visible spectrum has a shorter wavelength than most other colors, this effect is also commonly called a blue shift.
This can occur because of a change in environmental conditions: for example, a change in solvent polarity will result in solvatochromism. A series of structurally related molecules in a substitution series can also show a hypsochromic shift. Hypsochromic shift is a phenomenon seen in molecular spectra, not atomic spectra - it is thus more common to speak of the movement of the peaks in the spectrum rather than lines.
- where is the wavelength of the spectral peak of interest and
For example, β-acylpyrrole will show a hypsochromic shift of 30-40 nm in comparison with α-acylpyrroles.

See also[edit]
- Bathochromic shift, a change in band position to a longer wavelength (lower frequency).
