Medically reviewed by Drugs.com. Last updated on Aug 30, 2020.
In Summary
The patient is in shock.(correct; Doppler ultrasound is used to measure blood flow through the blood vessels when the patient's pulse is too feeble to be heard by a stethoscope. Shock is a life-threatening condition in which there is an excessive drop in blood pressure, which results in a feeble pulse.) The patient has prehypertension. Strong VS Weak Pulse: In my experience, patients usually cannot adequately evaluate there pulses. In the carotid area I would suggest getting a carotid ultrasound. If all is ok things are OK. Your blood pressure is another matter and is easily checked by yourself or even at a drug store with the machine there. Feeble Pulse ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index The ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index is designed to allow medical coders to look up various medical terms and connect them with the appropriate ICD codes. There are 0 terms under the parent term 'Feeble Pulse' in the ICD-10-CM Alphabetical Index.
Commonly reported side effects of ropivacaine include: hypotension and nausea. Other side effects include: bradycardia and vomiting. See below for a comprehensive list of adverse effects.
For the Consumer
Applies to ropivacaine: injection solution
Side effects requiring immediate medical attention
Along with its needed effects, ropivacaine may cause some unwanted effects. Although not all of these side effects may occur, if they do occur they may need medical attention.
Check with your doctor or nurse immediately if any of the following side effects occur while taking ropivacaine:
More common
- Blurred vision
- chest pain or discomfort
- confusion
- dizziness, faintness, or lightheadedness when getting up suddenly from a lying or sitting position
- lightheadedness, dizziness, or fainting
- slow or irregular heartbeat
- sweating
- unusual tiredness or weakness
Less common
- Burning, crawling, itching, numbness, prickling, 'pins and needles', or tingling feelings
- chills
- decrease in frequency or amount of urine
- difficulty in passing urine (dribbling)
- fever
- painful urination
Rare
- Absence of or decrease in body movement
- agitation
- bluish color of the skin or changes in skin color
- changes in vision
- clumsiness
- continuing ringing or buzzing or other unexplained noise in the ears
- cough
- decreased awareness or responsiveness
- difficulty breathing
- drooping upper eyelids
- drowsiness
- fast or irregular heartbeat
- general feeling of discomfort or illness
- loss of appetite
- loss of consciousness
- low body temperature
- mood or mental changes
- muscle aches
- muscle spasms (tetany) or twitching seizures
- muscle weakness
- nervousness
- noisy breathing
- pain or discomfort in the arms, jaw, back, or neck
- pain, redness, or swelling in the arm or leg
- problems with memory
- seeing or hearing things that are not there
- seizures
- severe sleepiness
- severe, unusual tiredness or weakness
- shivering
- swelling of the foot or leg tenderness
- tightness in the chest
- trembling
- trouble sleeping
- weak or feeble pulse
- weight gain
- yellow skin or eyes
Incidence not known
- Anxiety
- difficulty swallowing
- excitation
- fast, irregular, pounding, or racing heartbeat or pulse
- hives, itching, skin rash
- inability to breathe without assistance
- paralysis of the arms
- puffiness or swelling of the eyelids or around the eyes, face, lips, or tongue
- restlessness
- slow heartbeat
- tremors
Side effects not requiring immediate medical attention
Some side effects of ropivacaine may occur that usually do not need medical attention. These side effects may go away during treatment as your body adjusts to the medicine. Also, your health care professional may be able to tell you about ways to prevent or reduce some of these side effects.
Check with your health care professional if any of the following side effects continue or are bothersome or if you have any questions about them:
More common
Less common
- Anxiety
- runny or stuffy nose
- sneezing
Rare
- Bleeding, blistering, burning, coldness, discoloration of the skin, feeling of pressure, hives, infection, inflammation, itching, lumps, numbness, pain, rash, redness, scarring, soreness, stinging, swelling, tenderness, tingling, ulceration, or warmth at the injection site
- difficulty in moving
- frequent urge to defecate
- joint pain or swelling
- lack or loss of strength
- loss of bowel control
- muscle pain, cramps, or stiffness
- straining while passing stool
For Healthcare Professionals
Applies to ropivacaine: injectable solution
General
Reactions to this drug are characteristic of those associated with other amide-type local anesthetics. A major cause of side effects can me associated with excessive plasma levels which may be due to overdose, unintentional intravascular injection, or slow metabolic degradation.[Ref]
Cardiovascular
Very common (10% or more): Hypotension (up to 54.6%), bradycardia (up to 19.5%), fetal bradycardia (12.1%)
Common (1% to 10%): Hypertension, tachycardia, chest pain, fetal tachycardia, fetal distress
Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Syncope, severe hypotension
Rare (less than 0.1%): Cardiac arrest, cardiac arrhythmia
Frequency not reported: Vasovagal reaction, postural hypotension, non-specific ECG abnormalities, extrasystole, nonspecific arrhythmia, atrial fibrillation, ST segment changes, myocardial infarction, deep vein thrombosis, phlebitis, pulmonary embolism[Ref]
Nervous system
Common (1% to 10%): Paresthesia, headache, dizziness, hypoesthesia
Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): CNS toxicity, convulsion, grand mal convulsions, seizure, lightheadedness, circumoral paresthesia, numbness of the tongue, hyperacusis, dysarthria, tremor
Frequency not reported: Horner's syndrome, paresis, dyskinesia, neuropathy, coma, convulsion, hypokinesia, hypotonia, ptosis, stupor, spinal cord dysfunction, anterior spinal artery syndrome, arachnoiditis, cauda equine, total spinal block, persistent anesthesia, weakness, paralysis of lower extremities, loss of sphincter control, septic meningitis[Ref]
Local
Frequency not reported: Injection site pain[Ref]
Gastrointestinal
Very common (10% or more): Nausea (up to 29.4%), vomiting (up to 14.6%)
Common (1% to 10%): Neonatal vomiting
Frequency not reported: Fecal incontinence, tenesmus[Ref]
Other
Common (1% to 10%): Fever, pain, postoperative complication, rigors, neonatal complication, Apgar score low, neonatal fever, neonatal infection, temperature elevation, chills
Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Tinnitus, hypothermia, neonatal sepsis
Frequency not reported: Malaise, asthenia, accident/injury, hearing abnormal, vertigo[Ref]
Genitourinary
Common (1% to 10%): Urinary retention, oliguria, urinary tract infection, progression of labor poor/failed
Frequency not reported: Uterine atony, urinary incontinence, micturition disorder[Ref]
Dermatologic
Common (1% to 10%): Pruritus
Rare (less than 0.1%): Angioedema, urticaria
Frequency not reported: Rash[Ref]
Hematologic
Common (1% to 10%): Anemia[Ref]
Hepatic
Common (1% to 10%): Neonatal jaundice
Frequency not reported: Jaundice[Ref]

Metabolic
Common (1% to 10%): Hypokalemia, neonatal hypoglycemia
Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Fetal acidosis
Frequency not reported: Hypomagnesemia[Ref]
Musculoskeletal
Very common (10% or more): Back pain (up to 16.4%)
Common (1% to 10%): Cramps
Uncommon (0.1% to 1%): Muscular twitch, muscular rigidity, hypotonia
Frequency not reported: Myalgia[Ref]
Ocular
Frequency not reported: Vision abnormal, vision blurred, pupil constriction[Ref]
Psychiatric
Common (1% to 10%): Anxiety, insomnia
Frequency not reported: Agitation, confusion, somnolence, nervousness, amnesia, hallucination, emotional lability, nightmares, restlessness, drowsiness, unconsciousness[Ref]
Respiratory
Common (1% to 10%): Dyspnea, rhinitis, neonatal respiratory disorder, neonatal tachypnea, hypoxia, hypercapnia, apnea
Frequency not reported: Bronchospasm, coughing, underventilation, apnea, respiratory paralysis[Ref]
Endocrine
Common (1% to 10%): Breast disorder/breastfeeding disorder[Ref]
Immunologic
Rare (less than 0.1%): Allergic reaction, anaphylactic reaction[Ref]
References
1. 'Product Information. Naropin (ropivacaine).' Astra USA, Westborough, MA.
2. Cerner Multum, Inc. 'Australian Product Information.' O 0
Json for mac. 3. Cerner Multum, Inc. 'UK Summary of Product Characteristics.' O 0
More about ropivacaine
- During Pregnancy or Breastfeeding
Consumer resources
- Other brands
- Naropin, Naropin SDV, Naropin Polyamp
Professional resources
Related treatment guides
Further information
Always consult your healthcare provider to ensure the information displayed on this page applies to your personal circumstances.

Some side effects may not be reported. You may report them to the FDA.
Author Ольга Кияница
2018-05-16
Content
A weak pulse in the medical language is defined as a 'bradycardia.'Most often, if you have it, there are no special difficulties with your health.A person may feel a slight weakness, but overall the condition will be good.But sometimes, in addition to a weak pulse, low blood pressure is determined, and then a less favorable prognostic conclusion is given.
The average pulse rate is 60-100 beats per minute, although 55 and 45 beats / min may be considered a variant of the norm, if a person feels well at the same time.
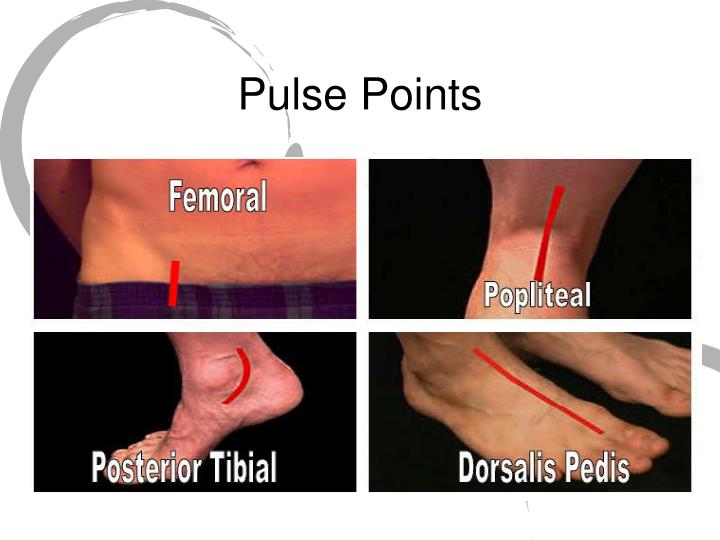
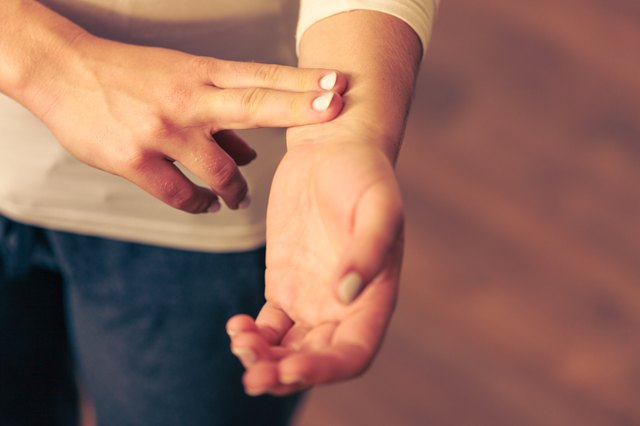
The pulse is determined quickly and easily.If you put the index and middle fingers on your wrist, you can feel the pulse and, after calculating the beats in one minute, you will know its frequency.With a rhythmic, even filling of the pulse, you can count not 60 sec, but 15 sec and after multiplying by 4 also find the desired index.
Video: Svetlana Strelnikova How to help the body if the weak pulse and bradycardia?
Causes of a weak pulse
There are serious diseases and pathological conditions, which are accompanied by a weak pulse.First of all it is:
- shock state;
- weakening of the body after long-term illnesses;
- lack of minerals and vitamins;
- various poisoning;
- supercooling;
- malformations, myocarditis and other heart diseases;
- brain tumors, meningitis and other pathologies of the nervous system.
A weak pulse can be observed during pregnancy, especially in the third trimester.This is often due to the fact that the increasing size of the uterus squeezes a hollow vein.If a woman besides a weak pulse does not bother anymore, then no specific treatment is required.
Girls who are long on a strict diet for weight loss can also celebrate a lowered pulse.Also, bradycardia occurs with internal bleeding, hormonal disorders, lack of physical activity or impaired nutrition.
Symptoms of a weak pulse
With a lowered pulse, there is insufficiently active blood circulation in various organs and systems, and the brain primarily suffers from this.
Cells do not receive enough oxygen and nutrients, which causes neurological disorders.
The main symptoms of a weak pulse:
- Decreased ability to work
- General weakness
- Dizziness
Vertigo is part of a larger symptom complex, which is most often associated with heart disease.Often occurs against the background of a bradycardia, when the electrical conductivity of the myocardium is disturbed.
Sometimes, hypothyroidism of the thyroid gland also determines a reduced pressure and a weak pulse.Such symptoms can develop with anemia, heart failure, and starvation.Also, some medications provoke a decrease in the pulse, and in severe cases - a cardiac arrest.
Additional symptoms of a weak pulse .
- Headache
With a combination of low heart rate and hypotension (low blood pressure), there is often a headache.It is characterized by a constant or paroxysmal course, against which the patient often has anxiety.This, in turn, further worsens his condition.In addition, there may be inferior sleep, bad mood and irritability.The provoking factors in such cases are nerve strains, inactivity, weather changes, infectious diseases.
Feeble Pulse Meaning
- Arrhythmia with a weak pulse
With a disturbed heart rhythm that developed against a background of a weak pulse, they talk about arrhythmia.In addition, the patient may be concerned about chest pain and shortness of breath.Quite often throws in cold sweat.A similar condition is a marker of another, more severe, cardiovascular disease.
- Low body temperature
Feeble Femoral Pulse
This symptom is often combined with a low pulse and may indicate a latent serious illness.Sometimes this change is preceded by a sharp decrease in hemoglobin in the blood.In other cases, dysfunction of the immune system or exacerbation of a chronic disease is determined.In addition to low temperature and a weak pulse, there may be inappropriate coordination, drowsiness, chills, and heightened anxiety.
Ways to normalize the pulse at home
When there is no way to get immediate medical attention, you can take appropriate measures to increase your pulse.
- Caffeinated products (boiled coffee, green tea, chocolate, espresso, cocoa)
Caffeine helps increase blood pressure and heart rate.But if a weak pulse is detected against a background of high blood pressure, then taking caffeine is not recommended.
- Tonic tinctures from ginseng, guarana, eleutherococcus
The effect of these drugs is manifested in increasing the tone of the body as a whole and blood pressure in particular.But it is necessary to take into account the same limitations as with caffeine, because often the pressure rises, while the pulse does not recover.
- Spicy food with horseradish, hot pepper or mustard
Seasonings of this type contribute to an improvement in blood flow, which indirectly affects the heart rate.It should be understood that this measure is not suitable for those who have problems with the gastrointestinal tract, since acute food contributes to exacerbation of inflammatory diseases of the digestive tract.
- Physical activity
Increase the pulse can help a little workout in the gym.The only thing, this variant does not approach at presence of heart diseases incompatible with fiznagruzkami.It happens that the pulse goes down due to lack of mobility (for example, a person just woke up or was on a long trip), in this case, light exercises or a walk in the fresh air will help.
- Mustard Compress
You can use a mustard plaster, which you need to attach to the right side of the chest.The created heat will start to stimulate the blood flow, which in turn will help normalize the pulse.
In extreme cases, when these methods do not help to normalize the pulse, medicines are used.These are sympathomimetic and anticholinergic drugs, which are prescribed by a doctor, while self-medication is fraught with side effects.
Medicamentous treatment of a weak pulse
In patients with a marked or suspected slow pulse, a thorough assessment of the possible causes described above should be made.Particular attention is paid to the list of drugs and potential factors of exposure.Laboratory and instrumental studies can be prescribed: a blood test, ultrasound of the thyroid gland.
An ECG is required, which allows you to determine the nature of the electrical activity of the heart as accurately as possible.
Sometimes Holter monitoring is assigned, in which a day or three are worn by a device that fixes the electrical activity of the heart throughout this time.Further, the analysis of the obtained data is carried out and a decision is made about the presence or absence of rhythm disorders.
Feeble Pulse Definition
Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) can be performed to evaluate the structure and function of the heart.
The tactics of treating a weak pulse depend on the severity and symptoms.First of all, the causes of the disorder and the possibility of their treatment or elimination are determined.If medications are ineffective, resort to the built-in driver rhythm.Installation of a pacemaker is carried out according to the following indications:
- Increased cardiac and myocardial weakness
- Long pauses in the heartbeat or rhythm that can lead to cardiac arrest.
The choice of a pacemaker for patients with a weak pulse depends on the individual characteristics of the individual patient and the severity of the blockade in carrying out cardiac pulses.
Video: What if the pulse is low?
